Chocolate is good for your health
Chocolate is good for your health . Chocolate is often associated with obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure, and other health.
Aditya Pandey

Chocolate is good for your health . Chocolate is often associated with obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure, and other health.

It's possible that your favourite piece of creamy and smooth chocolate is not good for you. Right? Chocolate is often associated with obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure, and other health issues like acne. This can be frustrating for chocolate lovers who love it. Chocolate consumption has many health benefits, which means that your nightly dose of dark chocolates could be good for your health.
Chocolate has long held a special place in the hearts of sweet-toothed individuals around the world. Beyond its delectable taste and undeniable allure, emerging research suggests that indulging in moderate amounts of chocolate may actually have several health benefits. In this article, we explore the potential positive effects of chocolate consumption on various aspects of health and well-being.
Rich in Antioxidants: Dark chocolate, in particular, is known for its high cocoa content, which is a rich source of antioxidants. Antioxidants help combat oxidative stress in the body, reducing the risk of chronic diseases and supporting overall health. Flavanols, a type of antioxidant found in chocolate, have been linked to improved heart health.
Heart Health and Blood Pressure: Several studies have suggested that regular consumption of Dark chocolate is Good For Heart may contribute to better cardiovascular health. The flavanols in chocolate may help relax blood vessels, improve blood flow, and reduce blood pressure. Maintaining healthy blood pressure levels is crucial for heart health and the prevention of cardiovascular diseases.
Mood Enhancement: Chocolate is often associated with feelings of happiness and pleasure, and there's a scientific reason behind it. Chocolate contains compounds such as phenylethylamine and serotonin precursors that can stimulate the release of endorphins in the brain. Endorphins are neurotransmitters responsible for creating feelings of happiness and reducing stress.
Brain Health and Cognitive Function: Flavanols found in chocolate may have positive effects on cognitive function and brain health. Some studies suggest that regular consumption of cocoa-rich products may improve memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. The potential neuroprotective benefits of chocolate make it an intriguing subject in ongoing research on brain health.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Chronic inflammation is associated with various health issues, including cardiovascular diseases and certain types of cancer. Dark chocolate, with its anti-inflammatory properties, may help reduce inflammation in the body. This anti-inflammatory effect contributes to an overall healthier internal environment.
Mineral Content: Chocolate contains essential minerals, including magnesium, copper, and iron. Magnesium is crucial for muscle and nerve function, copper supports the immune system, and iron is essential for transporting oxygen in the blood. While chocolate should not be relied upon as a primary source of these minerals, it can contribute to overall mineral intake in moderation.
Weight Management: Contrary to common belief, moderate chocolate consumption may not necessarily lead to weight gain. Dark chocolate, in particular, tends to be more satisfying and less likely to trigger excessive eating compared to milk chocolate. Additionally, the satisfaction derived from indulging in a small amount of chocolate may help curb cravings for other less healthful sweets.
Reduced Risk of Stroke: Some studies have suggested a potential link between chocolate consumption and a reduced risk of stroke. The flavonoids in chocolate may have protective effects on the vascular system, contributing to improved blood flow and reducing the risk of blood clots.
While the health benefits of chocolate are increasingly recognized, it's essential to emphasize moderation in consumption. Not all chocolate varieties are created equal, and the benefits are most pronounced in dark chocolate with a high cocoa content. Incorporating small amounts of quality chocolate into a balanced diet, along with regular exercise and other healthy lifestyle choices, can contribute to a sweet and healthful life. As with any dietary considerations, individuals should consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice based on their health status and specific needs. So, the next time you savor a piece of chocolate, take comfort in the fact that you might just be treating yourself to more than just a delightful taste.

How often can you have chocolate?
The frequency with which you can enjoy chocolate largely depends on various factors, including the type of chocolate, its cocoa content, your overall diet, and individual health considerations. While chocolate can offer health benefits in moderation, it's crucial to strike a balance to prevent excessive calorie and sugar intake. Here are more details on how often you can have chocolate:
Consider Cocoa Content: The health benefits of chocolate are often associated with dark chocolate, which has a higher cocoa content. Cocoa is rich in antioxidants, particularly flavonoids, that contribute to its positive effects on heart health and overall well-being. Opt for dark chocolate with at least 70% cocoa for maximum health benefits.
Moderation is Key: Enjoying chocolate in moderation is the key to incorporating it into a healthy diet. While there is no one-size-fits-all recommendation, consuming a small portion of Types Of chocolate a few times per week is generally considered reasonable. This allows you to savor the treat without overindulging.
Caloric Considerations: Chocolate, especially milk chocolate and those with added ingredients like caramel or nuts, can be calorie-dense. It's important to be mindful of your overall caloric intake and ensure that your chocolate consumption fits into your daily calorie budget. This is particularly relevant if you are working towards weight management or weight loss goals.
Nutritional Profile: Dark chocolate contains minerals such as magnesium, copper, and iron, along with antioxidants. However, it's not a significant source of essential nutrients. It's advisable to obtain essential nutrients from a varied and balanced diet that includes a range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
Individual Health Factors: Individual health factors, such as pre-existing conditions or dietary restrictions, should be considered. Individuals with conditions like diabetes should be cautious about chocolate consumption due to its sugar content. Those with allergies or sensitivities should choose chocolate products that align with their dietary needs.
Quality Over Quantity: When it comes to chocolate, prioritize quality over quantity. Higher quality chocolates, especially those with a higher cocoa content, tend to be more satisfying, allowing you to enjoy smaller portions. Opting for a piece of rich, dark chocolate may be more satisfying than consuming larger quantities of lower-quality chocolate.
Mindful Eating: Practice mindful eating when enjoying chocolate. Savor the flavors and textures, and be present in the moment. This approach can enhance the overall enjoyment of the treat and may reduce the likelihood of overconsumption.
Balance with a Healthy Diet: Chocolate should be seen as a part of an overall healthy diet. It's essential to balance chocolate consumption with a variety of nutrient-dense foods to ensure that your nutritional needs are met. A well-rounded diet provides a range of vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients.
Physical Activity: Regular physical activity can play a role in how often you can indulge in chocolate. Incorporating exercise into your routine helps burn calories and contributes to overall well-being, allowing for occasional treats without compromising your health goals.
Consult with Healthcare Professionals: If you have specific health concerns or conditions, it's advisable to consult with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians. They can provide personalized guidance based on your health status, dietary preferences, and overall lifestyle.
A healthy person can eat chocolate every day. It all depends on how much and what it is made of. Bitter chocolate contains at least 60% cocoa, making it the most useful. Cocoa beans are high in magnesium and dietary fibre, so they promote the release of endorphins, which are essential to fight stress. Even a small amount of healthy dark chocolate can help you feel calmer and more relaxed. Be aware that cocoa contains caffeine, which can increase blood pressure. 40g of dark chocolate is equivalent to a cup of strong coffee. Milk chocolate bars and candies should be avoided before going to bed. These candies and bars are high in sugar and fats that can cause damage to tooth enamel and increase your risk of developing cardiovascular disease.

Chocolate is good for your health
Certainly! Chocolate, particularly dark chocolate with high cocoa content, has been associated with several health benefits when consumed in moderation. Here are more details on why chocolate can be considered good for your health:
Rich in Antioxidants: Cocoa, the main ingredient in chocolate, is packed with antioxidants. Antioxidants help neutralize free radicals in the body, which can reduce oxidative stress and inflammation. This, in turn, may contribute to the prevention of chronic diseases.
Heart Health: Numerous studies suggest that dark chocolate may have positive effects on heart health. Flavanols, a type of antioxidant present in cocoa, may help improve blood flow, lower blood pressure, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Regular consumption of dark chocolate has been linked to a lower risk of heart-related issues.
Improved Cholesterol Levels: Dark chocolate may contribute to improved cholesterol profiles. Some studies indicate that it can increase levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL or "good" cholesterol) while reducing levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL or "bad" cholesterol), promoting a healthier balance.
Enhanced Mood and Brain Function: Chocolate contains compounds such as phenylethylamine and serotonin precursors that can stimulate the release of endorphins in the brain. Endorphins are neurotransmitters responsible for creating feelings of happiness and reducing stress. Additionally, certain studies suggest that chocolate may have positive effects on cognitive function and memory.
Reduced Risk of Stroke: Some research indicates that regular consumption of chocolate may be associated with a lower risk of stroke. The flavonoids in chocolate have been linked to improved blood flow and reduced clot formation, contributing to better vascular health.
Source of Essential Minerals: Chocolate, especially dark chocolate, contains essential minerals like magnesium, copper, and iron. Magnesium is crucial for muscle and nerve function, copper supports the immune system, and iron is essential for oxygen transport in the blood.
Antidepressant Effects: The compounds in chocolate, including serotonin precursors, may have mild antidepressant effects. While chocolate is not a substitute for professional mental health care, it can contribute to feelings of relaxation and pleasure.
Blood Sugar Regulation: Dark chocolate, in moderation, may have a mild impact on blood sugar levels. The flavonoids in chocolate may improve insulin sensitivity, potentially helping with blood sugar regulation. However, individuals with diabetes should still consume chocolate cautiously and in moderation.
Reduced Inflammation: The anti-inflammatory properties of chocolate, attributed to its antioxidant content, may contribute to reduced inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is linked to various health issues, and incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, such as dark chocolate, can be beneficial.
Improved Endothelial Function: Flavanols in chocolate have been shown to enhance endothelial function, which refers to the health of the inner lining of blood vessels. Improved endothelial function is associated with better vascular health and reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Moderation and Quality Matters: While these potential health benefits are associated with chocolate, it's crucial to emphasize moderation and choose high-quality, dark chocolate with minimal added sugars. Excessive consumption of chocolate, especially varieties with lower cocoa content and higher sugar content, can lead to negative health effects.
Consultation with Healthcare Professionals: Individuals with specific health conditions or dietary concerns should consult with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians for personalized advice. They can provide guidance based on individual health status, dietary needs, and overall lifestyle.
Chocolate lovers rejoice! Getting lost in all the claims about chocolate's health benefits is easy. Who doesn't like a square or a bar of chocolate? It's important to eat chocolate as a whole. If you overeat chocolate, the potential health benefits may be negated. Limit your daily chocolate intake to just one or two squares per day. You should take the time to enjoy each bite of chocolate. To the health benefits of chocolate, choose chocolate with a higher percentage of cocoa. Dark chocolate is best chocolate for health. Dark chocolate should contain at least 70% cocoa. Dark chocolate bars that contain higher amounts of cocoa are more likely to have lower sugar levels.
You don't have to stop eating chocolate because it is high in sugar and fat. The cocoa content of chocolate has been shown in studies to improve specific health indicators. For the best results, choose dark chocolate and limit how much you consume.

It can help you lose weight
While chocolate is generally associated with being high in calories and sugar, certain types of chocolate, specifically dark chocolate with high cocoa content, may have attributes that could potentially support weight loss when consumed in moderation. Here are more details on how chocolate, particularly dark chocolate, may be linked to weight management:
Satiety and Portion Control: Dark chocolate, with its rich flavor and higher cocoa content, tends to be more satisfying in smaller quantities compared to milk chocolate. The intensity of the taste may lead to greater satisfaction, potentially reducing the desire to consume larger portions or indulge in additional snacks.
Reduced Cravings: The sensory pleasure derived from consuming dark chocolate may help curb cravings for other sweets. A small piece of dark chocolate can provide a satisfying sweetness, potentially reducing the temptation to reach for higher-calorie and less nutritious snacks.
Mindful Eating Practices: Enjoying chocolate mindfully, savoring each bite, can contribute to a more conscious approach to eating. Mindful eating has been linked to improved weight management by promoting a better understanding of hunger and fullness cues, preventing overeating.
Potential Impact on Metabolism: Some studies suggest that the compounds found in dark chocolate, such as catechins and caffeine, may have a modest impact on metabolism. While the effects are not dramatic, a slightly increased metabolic rate could contribute to the overall calorie-burning process.
Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Flavonoids in dark chocolate have been associated with improved insulin sensitivity. Better insulin sensitivity can support more stable blood sugar levels, potentially reducing cravings for sugary foods and aiding in weight management.
Mind-Body Connection: The pleasurable experience of enjoying a small piece of dark chocolate may positively influence mood. Emotional well-being can play a role in weight management, as individuals with a more positive mindset may find it easier to adhere to a healthy lifestyle.
Balanced Indulgence: Incorporating small amounts of dark chocolate into a well-balanced diet can offer a sense of indulgence without derailing weight management efforts. This approach helps avoid feelings of deprivation, which can lead to overeating or bingeing on less healthy options.
High Nutrient Density: Dark chocolate contains essential minerals such as magnesium, copper, and iron. While it's not a primary source of these nutrients, including dark chocolate as part of a nutrient-dense diet contributes to overall nutritional intake.
Calorie Awareness: Choosing high-quality dark chocolate often means fewer added sugars and less saturated fat compared to other chocolate varieties. Being mindful of calorie intake is crucial for weight management, and opting for dark chocolate allows for a sweet treat with potentially fewer calories.
Exercise Motivation: Some studies suggest that the flavonoids in dark chocolate may improve exercise performance by enhancing oxygen utilization and blood flow. Improved exercise performance can contribute to overall weight management efforts.
It's important to note that while dark chocolate may have certain attributes that could support weight management, it should be part of a broader healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular physical activity. Additionally, individual responses to chocolate can vary, and moderation remains key to avoiding excessive calorie intake.
Will Clower, a neuroscientist, believes that chocolate doesn't need to be the reason for weight gain. Clower explains in his book Eat Chocolate, Lose Weight how eating dark chocolate 20 minutes before or five minutes after a meal can reduce appetite by up to 50%. Dark chocolate is best chocolate for weight loss. Clower says this happens because chocolate triggers hormones in your brain that tell you, "I'm full." But this only applies to cacao-rich, dark chocolate, and you would feel even more compelled to eat milk chocolate, which will raise your blood sugar and cause you to crave it.

Chocolate may help combat Diabetes
While it might seem counterintuitive due to the sugar content in chocolate, there is some evidence suggesting that dark chocolate, in moderation, may have certain benefits for individuals with Diabetes and Sugar Free Chocolate . It's essential to emphasize that the type of chocolate and portion control are crucial factors. Here are more details on how chocolate, particularly dark chocolate, may be associated with potential benefits for diabetes management:
Low Glycemic Index: Dark chocolate has a lower glycemic index compared to milk chocolate or other sugary treats. The glycemic index measures how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. Foods with a lower glycemic index lead to a slower and more controlled increase in blood glucose levels, which can be beneficial for individuals with diabetes.
Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Some studies suggest that the flavonoids present in dark chocolate may enhance insulin sensitivity. Improved insulin sensitivity means that the body can use insulin more effectively to regulate blood sugar levels. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with insulin resistance, a common condition in type 2 diabetes.
Reduced Insulin Resistance: Dark chocolate consumption has been associated with a reduction in insulin resistance in some research studies. Lower insulin resistance is a positive outcome for individuals with type 2 diabetes as it helps improve the body's ability to respond to insulin.
Antioxidant Properties: Dark chocolate is rich in antioxidants, particularly flavonoids. Antioxidants help combat oxidative stress, which is linked to inflammation and complications associated with diabetes. By reducing oxidative stress, dark chocolate may contribute to overall diabetes management.
Cardiovascular Health Benefits: Individuals with diabetes are often at a higher risk of cardiovascular complications. Dark chocolate has been linked to improvements in cardiovascular health, including lower blood pressure and improved cholesterol levels. These cardiovascular benefits can be advantageous for those with diabetes.
Mindful Indulgence: Including small portions of dark chocolate in a diabetes-friendly diet can provide a sense of indulgence without causing significant spikes in blood sugar levels. This mindful approach to sweet treats may help individuals adhere to a balanced and sustainable eating plan.
Polyphenol Content: Dark chocolate contains polyphenols, which have anti-inflammatory and potential blood sugar-regulating properties. These polyphenols may contribute to the overall positive effects of dark chocolate on insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control.
Blood Sugar Moderation: Dark chocolate, when consumed in moderation, may have a modest impact on blood sugar levels. This is attributed to its composition, including lower sugar content and the presence of fiber, which can slow the absorption of sugar.
Quality Matters: Opting for high-quality dark chocolate with a cocoa content of at least 70% ensures that you are getting more of the potential health benefits and fewer added sugars. Checking the ingredient list is crucial to avoid chocolates with excessive sugars or unhealthy additives.
Consultation with Healthcare Professionals: Individuals with diabetes should consult with their healthcare professionals or registered dietitians for personalized advice. Recommendations may vary based on individual health status, medications, and specific dietary needs.
Diabetic chocolates seems to be an unlikely partner in the fight against diabetes, and one study suggests that chocolate bars may hold the key to beating diabetes. Research shows that certain chocolate compounds can increase insulin sensitivity and help with blood sugar control.
Researchers conducted their experiment with animals by feeding them high-fat diets high in epicatechin monomers (compounds found in cocoa) and high-fat diets. The researchers discovered that cocoa compounds helped beta cells to secrete insulin more quickly by examining the tiny interactions between cells.
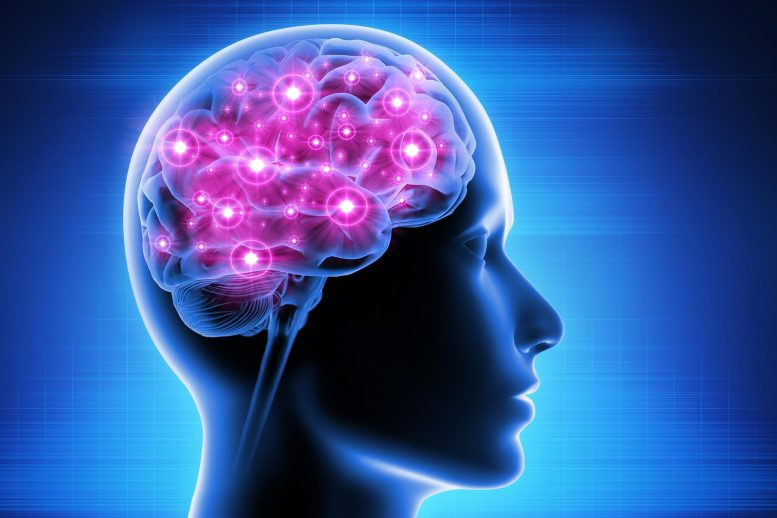
It Improves Brain Health and Prevents Mental Decline
Dark chocolate, with its rich cocoa content, contains compounds that have been associated with potential benefits for brain health and may play a role in preventing mental decline. Here are more details on how dark chocolate could contribute to improved cognitive function and overall brain health:
Rich in Flavonoids: Dark chocolate is abundant in flavonoids, a group of antioxidant compounds found in plants. Flavonoids, specifically flavanols, are thought to have neuroprotective effects and contribute to improved blood flow to the brain.
Enhanced Blood Flow to the Brain: The flavanols in dark chocolate may stimulate the production of nitric oxide, which can help relax blood vessels. This relaxation leads to increased blood flow, including to the brain. Improved blood flow is associated with better cognitive function and may contribute to the prevention of mental decline.
Improved Cognitive Function: Some studies suggest that regular consumption of dark chocolate may be linked to improvements in cognitive function. This includes aspects such as memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. The positive effects are attributed to the flavonoids and other bioactive compounds in chocolate.
Neuroprotective Properties: The antioxidants in dark chocolate have neuroprotective properties, potentially shielding the brain from oxidative stress and inflammation. Oxidative stress is implicated in the aging process and various neurodegenerative conditions, including Alzheimer's disease.
Increased Production of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF): Dark chocolate consumption has been associated with increased levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). BDNF is a protein that supports the growth, survival, and differentiation of neurons. Higher levels of BDNF are linked to improved cognitive function and may contribute to neuroplasticity.
Positive Effects on Mood: Chocolate contains compounds that can positively impact mood. Phenylethylamine, one of these compounds, is known as the "love hormone" and may contribute to feelings of happiness and pleasure. A positive mood can have indirect benefits on cognitive function.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Chronic inflammation is associated with cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases. The anti-inflammatory properties of dark chocolate's antioxidants may help mitigate inflammation in the brain, providing additional protection against mental decline.
Potential for Long-Term Cognitive Health: While research is ongoing, some studies suggest that regular, moderate consumption of dark chocolate over the long term may have cumulative effects on cognitive health. It's important to note that these effects are likely to be part of a broader lifestyle approach that includes a healthy diet and regular physical activity.
Optimal Cocoa Content: To maximize potential brain health benefits, it's recommended to choose dark chocolate with a high cocoa content, ideally at least 70%. The higher the cocoa content, the more flavonoids and antioxidants the chocolate is likely to contain.
Moderation is Key: While dark chocolate may offer potential cognitive benefits, moderation is crucial. Excessive consumption can lead to an overabundance of calories and sugars, which can have negative effects on overall health.
Individual Variability: Responses to dark chocolate's potential cognitive benefits may vary among individuals. Factors such as age, genetics, overall diet, and lifestyle can influence the extent of these effects.
Consultation with Healthcare Professionals: Individuals seeking to enhance brain health through dietary choices, including the consumption of dark chocolate, should consult with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians. Personalized advice can be tailored to individual health status and dietary needs.
According to a study, chocolate can improve memory and other cognitive functions and even prevent mental decline when consumed regularly Scientists found that cocoa consumption daily increased attention, memory, processing speed and verbal fluency The greatest benefits were seen in people with mild mental decline and memory impairment.
Dark chocolate is rich in flavanols We should always have some dark chocolate, and the authors explain that they eat dark chocolate every day Dark chocolate is good for health and While chocolate can be good for your brain, there are other side effects due to the high amount of calories Cocoa contains caffeine, and the Sugar Free Chocolate levels in chocolate products may be higher if they are made with milk or other sugars.
Writer and content creator
Log in to share your thoughts and engage with other readers.